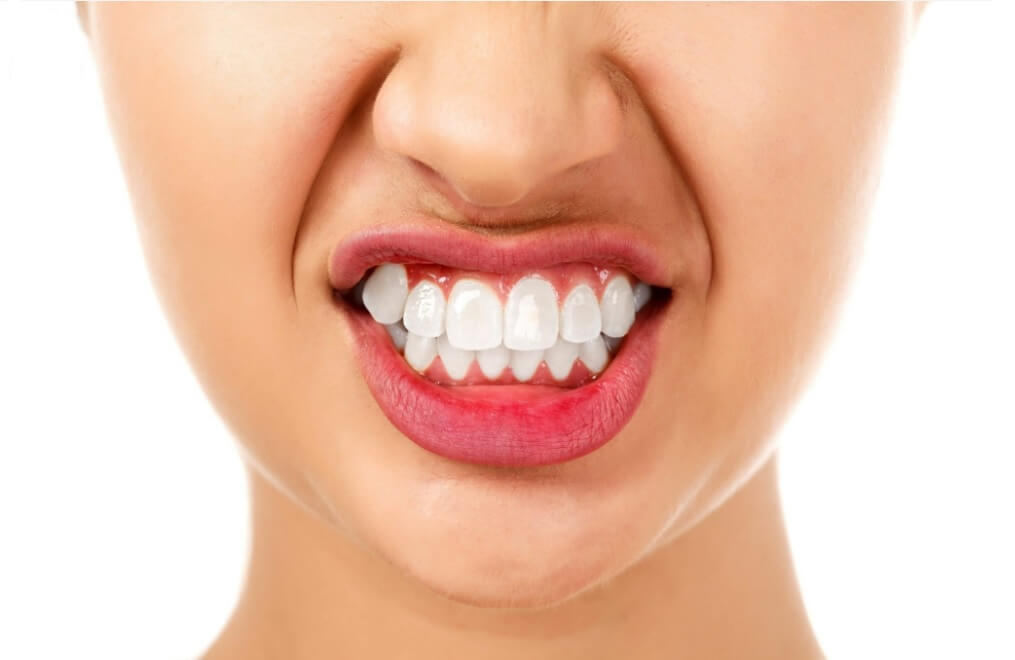
Bruxism, better known as teeth grinding, often occurs during sleep. This is why it is often called nocturnal or sleep bruxism. For some people, however, they also subconsciously clench their jaw and grind their teeth while awake. This is called awake bruxism or daytime bruxism.
Clenching teeth while awake may not seem that much, but it can actually lead to a lot of health concerns, such as teeth sensitivity due to worn tooth enamel. Sometimes it can even lead to temporomandibular disorder (TMD) or pain in the jaw joint and the muscles that control that jaw movement.
What daytime bruxism means
The exact cause of teeth grinding isn’t always clear. However, there are links to different factors, such as anxiety, stress, sleep problems, medication, excessive intake of alcohol or caffeine, and even lifestyle.
- Stress and anxiety – Bruxism is often caused by stress and anxiety. It is often linked to emotionally stressful jobs such as those in healthcare, law enforcement, military, etc.
- Medicine – Some medications often cause bruxism as a side-effect, especially antidepressants (i.e. selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor or SSRI).
- Lifestyle – Other common factors include excessive intake of alcohol, caffeine, recreational drugs (cocaine, ecstasy), and smoking can lead to teeth grinding.
- Misaligned bite – Crooked, missing teeth and misaligned teeth can also lead to daytime bruxism.

What to do to avoid daytime bruxism
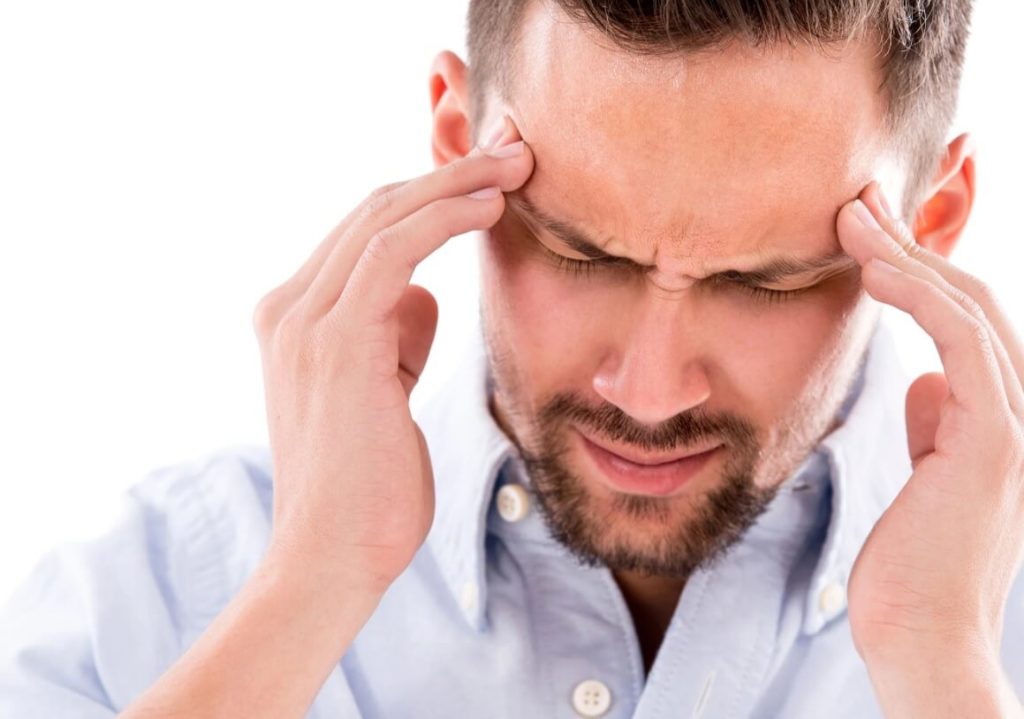
As said earlier, clenching teeth while awake can lead to multiple health complications, such as loose or fractured, worn down teeth and even loss of teeth. This could lead to the need for bridges, crowns, or even dentures and implants. Other painful symptoms include:
- Earache
- Headache
- Facial pain
- Pain and/or stiffness in the jaw joint and muscles surrounding the jaw (could lead to TMD)
So what can you do to avoid daytime bruxism?
Since stress is the most common factor, managing and avoiding stress is the first thing you can do to prevent teeth grinding. Stress reduction activities such as exercise, yoga, deep breathing, and meditation can all help discourage teeth clenching. Also, relaxing treatments like acupuncture and massage can help reduce stress. Your general practitioner can help you better manage stress, as well.
It is best to avoid or limit your alcohol and caffeine consumption, and even quit smoking (if you do smoke).
You may also consider checking with your dentist for an orthodontic treatment, as misaligned or missing teeth can contribute to bruxism. It is important to see your dentist if you notice teeth sensitivity or if you notice any signs of damage. This is to avoid further complications like infection or dental abscess.
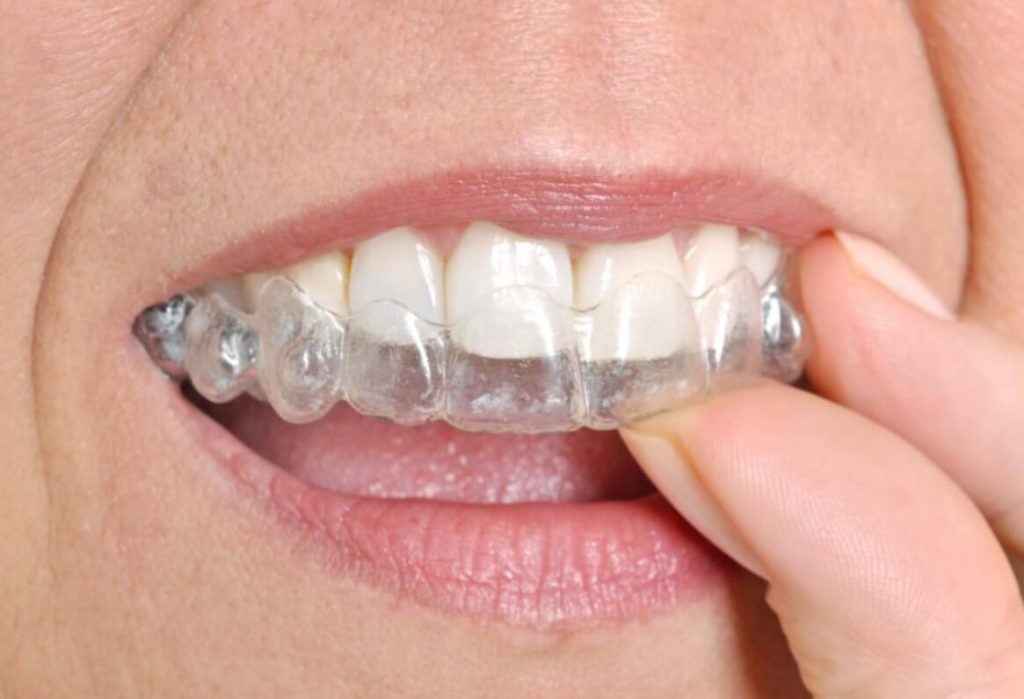
How dentists treat bruxism
If you find yourself grinding your teeth during daytime, chances are you also do it at night. The most common treatment for nighttime bruxism is wearing a special mouth guard fitted by a TMJ specialist. This can help protect your teeth from grinding, as well as the muscles, tissue, and bones in your jaw.
For misaligned, crooked, and/or crowded teeth, dentists can perform reductive coronoplasty to reshape or level your bite surface.
In severe cases, and often a last result treatment for patients who experience severe pain or difficulty in opening their mouth, dentists will prescribe muscle relaxant. Taken before bedtime, this medication relaxes the muscles and keeps you from clenching your jaw and grinding your teeth. In most cases, however, a mouth guard can suffice to discourage patients from grinding their teeth.
Whether you are clenching your teeth while awake or during night, it is something that you cannot afford to ignore. See an expert immediately so that you can discuss possible treatment options.
























